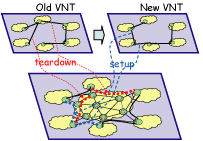
Figure 1: VNT-based traffic engineering
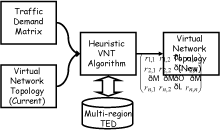
Figure 2: General flow diagram of the VNT algorithm
GMPLS-based traffic engineering in multi-region/multi-layer service network
Kohei Shiomoto (Speaker) and Takashi Kurimoto
NTT Network Service Systems Laboratories
GMPLS extends MPLS to various switching technologies including PSC, TDM, LSC, and FSC devices by introducing the concept of "switching capability". GMPLS-based network, which consists of multiple switching capabilities, are referred to as "multi-region network". Since GMPLS is a common set of protocols to control these switching networks, the network resources are efficiently utilized by using GMPLS to control all network resources between multiple regions.
In this presentation we address the multi-layer service network concept as well as GMPLS-based multi-region network, and the traffic engineering in the proposed network. Multi-region network enables different capability (layer) connections treated in a seamless way so that efficient resource usage and traffic engineering can be realized over such different layer regions with GMPLS technology. Multi-layer service network extend GMPLS based multi-region network to accommodate several independent service networks, which have no GMPLS capability.
Traffic engineering in multi layer network should have features which handles different layers' traffic and resource information for maximum efficiency in the traffic engineering. GMPLS has a key role to enable multi layer resource handling both for the GMPLS-based multi-region/multi -layer network at the border between non-GMPLS capable service networks. In particular, we demonstrate the virtual network topology (VNT)-based traffic engineering, where a set of light-paths provides the virtual network topology for the IP-layer routing/traffic engineering (Fig. 1)
By reconfiguring the virtual network topology according the traffic demand between source-destination node pairs, the network performance such as maximum link utilization and residual capacity of the network is optimized. The virtual network topology is reconfigured by setting up and/or tearing down the light-paths (lambda-LSPs) in the GMPLS-based multi-region network. When this optical path reconfiguration occurs, router has to negotiate the IGP adjacency and IP routing table has to be re-constructed. This indicates that IP network will become unstable. To avoid unstable state, a correlating function is proposed to hide this optical path reconfiguration from legacy network. We describe protocols and mechanisms facilitating the concept
Virtual network topology (VNT) algorithm is a key component in the traffic-engineering in GMPLS-based multi-region network. The VNT algorithm computes the new VNT from the current VNT and the traffic demand matrix under constraint of the multi-region traffic engineering database (MR-TED) (See Fig. 2). Heuristic algorithm is tailored according to the service provider's policy regarding the network performance and quality of service (delay, loss/disruption, utilization, residual capacity, reliability). We discuss the pros and cons of heuristic algorithms.
Finally, to give the perspective of the multi-region and multi-layer traffic engineering, we address the taxonomy of the multi-region and multi-layer traffic-engineering with respect to approach (layered and mixed) and network architecture (vertical and horizontal). We address the future direction in the traffic engineering in multi-layer service network.
 Figure 1: VNT-based traffic engineering |
 Figure 2: General flow diagram of the VNT algorithm |